Control and Coordination
Solutions of Science Exemplar Problems
Multiple Choice Questions
1. Which of the following statements is correct about receptors?
(a) Gustatory receptors detect taste while olfactory receptors detect smell
(b) Both gustatory and olfactory receptors detect smell
(c) Auditory receptors detect smell and olfactory receptors detect taste
(d) Olfactory receptors detect taste and gustatory receptors smell
2. Electrical impulse travels in a neuron from
(a) Dendrite → axon → axonal end → cell body
(b) Cell body → dendrite → axon → axonal end
(c) Dendrite → cell body → axon → axonal end
(d) Axonal end → axon → cell body → dendrite
3. In a synapse, chemical signal is transmitted from
(a) dendritic end of one neuron to axonal end of another neuron
(b) axon to cell body of the same neuron
(c) cell body to axonal end of the same neuron
(d) axonal end of one neuron to dendritic end of another neuron
4. In a neuron, conversion of electrical signal to a chemical signal occurs at/in
(a) cell body
(b) axonal end
(c) dendritic end
(d) axon
5. Which is the correct sequence of the components of a reflex arc?
(a) Receptors→ Muscles→ Sensory neuron→ Motor neuron→ Spinal cord
(b) Receptors→ Motor neuron → Spinal cord → Sensory neuron → Muscle
(c) Receptors → Spinal cord → Sensory neuron → Motor neuron → Muscle
(d) Receptors → Sensory neuron → Spinal cord → Motor neuron → Muscle
6. Which of the following statements are true?
(i) Sudden action in response to something in the environment is
called reflex action
(ii) Sensory neurons carry signals from spinal cord to muscles
(iii) Motor neurons carry signals from receptors to spinal cord
(iv) The path through which signals are transmitted from a receptor
to a muscle or a gland is called reflex arc
(a) (i) and (ii) (b) (i) and (iii)
(c) (i) and (iv) (d) (i) , (ii) and (iii)
7. Which of the following statements are true about the brain?
(i) The main thinking part of brain is hind brain
(ii) Centres of hearing, smell, memory, sight etc are located in fore
brain.
(iii) Involuntary actions like salivation, vomiting, blood pressure
are controlled by the medulla in the hind brain
(iv) Cerebellum does not control posture and balance of the body
(a) (i) and (ii) (b) (i), (ii) and (iii)
(c) (ii) and (iii) (d) (iii) and (iv)
8. Posture and balance of the body is controlled by
(a) cerebrum
(b) cerebellum
(c) medulla
(d) pons
9. Spinal cord originates from
(a) cerebrum
(b) medulla
(c) pons
(d) cerebellum
10. The movement of shoot towards light is
(a) geotropism
(b) hydrotropism
(c) chemotropism
(d) phototropism
11. The main function of abscisic acid in plants is to
(a) increase the length of cells
(b) promote cell division
(c) inhibit growth
(d) promote growth of stem
12. Which of the following is not associated with growth of plant?
(a) Auxin
(b) Gibberellins
(c) Cytokinins
(d) Abscisic acid
13. Iodine is necessary for the synthesis of which hormone?
(a) Adrenaline
(b) Thyroxin
(c) Auxin
(d) Insulin
14. Choose the incorrect statement about insulin
(a) It is produced from pancreas
(b) It regulates growth and development of the body
(c) It regulates blood sugar level
(d) Insufficient secretion of insulin will cause diabetes
15. Select the mis-matched pair
(a) Adrenaline : Pituitary gland
(b) Testosterone: Testes
(c) Estrogen : Ovary
(d) Thyroxin : Thyroid gland
16. The shape of guard cells changes due to change in the
(a) protein composition of cells
(b) temperature of cells
(c) amount of water in cells
(d) position of nucleus in the cells
17. The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to
(a) effect of light
(b) effect of gravity
(c) rapid cell divisions in tendrillar cells that are away from the
support
(d) rapid cell divisions in tendrillar cells in contact with the support
18. The growth of pollen tubes towards ovules is due to
(a) hydrotropism
(b) chemotropism
(c) geotropism
(d) phototropism
19. The movement of sunflower in accordance with the path of sun is
due to
(a) phototropism
(b) geotropism
(c) chemotropism
(d) hydrotropism
20. The substance that triggers the fall of mature leaves and fruits
from plants is due to
(a) auxin
(b) gibberellin
(c) abscisic acid
(d) cytokinin
21. Which of the following statements about transmission of nerve
impulse is incorrect?
(a) Nerve impulse travels from dendritic end towards axonal end
(b) At the dendritic end electrical impulses bring about the release
of some chemicals which generate an electrical impulse at the
axonal end of another neuron
(c) The chemicals released from the axonal end of one neuron cross
the synapse and generate a similar electrical impulse in a
dendrite of another neuron
(d) A neuron transmits electrical impulses not only to another
neuron but also to muscle and gland cells
22. Involuntary actions in the body are controlled by
(a) medulla in fore brain
(b) medulla in mid brain
(c) medulla in hind brain
(d) medulla in spinal cord
23. Which of the following is not an involuntary action?
(a) Vomiting
(b) Salivation
(c) Heart beat
(d) Chewing
24. When a person is suffering from severe cold, he or she cannot
(a) differentiate the taste of an apple from that of an ice cream
(b) differentiate the smell of a perfume from that of an agarbatti
(c) differentiate red light from green light
(d) differentiate a hot object from a cold object
26. Which statement is not true about thyroxin?
(a) Iron is essential for the synthesis of thyroxin
(b) It regulates carbohydrates, protein and fat metabolism in the body
(c) Thyroid gland requires iodine to synthesise thyroxin
(d) Thyroxin is also called thyroid hormone
27. Dwarfism results due to
(a) Excess secretion of thyroxin
(b) Less secretion of growth hormone
(c) Less secretion of adrenaline
(d) Excess secretion of growth hormone
28. Dramatic changes of body features associated with puberty are
mainly because of secretion of
(a) oestrogen from testes and testosterone from ovary
(b) estrogen from adrenal gland and testosterone from pituitary gland
(c) testosterone from testes and estrogen from ovary
(d) testosterone from thyroid gland and estrogen from pituitary gland
29. A doctor advised a person to take an injection of insulin because
(a) his blood pressure was low
(b) his heart was beating slowly
(c) he was suffering from goitre
(d) his sugar level in blood was high
30. The hormone which increases the fertility in males is called
(a) oestrogen
(b) testosterone
(c) insulin
(d) growth hormone
31. Which of the following endocrine glands is unpaired?
(a) Adrenal
(b) Testes
(c) Pituitary
(d) Ovary
32. Junction between two neurons is called
(a) cell junction
(b) neuro muscular junction
(c) neural joint
(d) synapse
33. In humans, the life processes are controlled and regulated by
(a) reproductive and endocrine systems
(b) respiratory and nervous systems
(c) endocrine and digestive systems
(d) nervous and endocrine systems
Ans.
Short Answers Question
Ans.34. (a) Sensory neuron
(b) Spinal cord (CNS)
(c) Motor neuron
(d) Effector = Muscle in arm
35. Name the plant hormones responsible for the following
(a) elongation of cells
(b) growth of stem
(c) promotion of cell division
(d) falling of senescent leaves.
Ans35. (a) Auxin
(b) Gibberellin
(c) Cytokinin
(d) Abscisic acid
36. Label the endocrine glands in Figure 7.3.
Ans.36. (a) Pineal gland (b) Pituitary gland (c) Thyroid (d) Thymus
37. Figure (a) is more appropriate because in a plant shoots are
negatively geotropic hence, grow upwards and roots are positively
geotropic so grow downwards.
38. (a) Dendrite
(b) Cell body
(c) Axon
(d) Nerve ending

Ans.39. (a) — (iii) (b) — (iv) (c) — (i) (d) — (ii)
.
40. What is a tropic movement? Explain with an example.
Ans.40. The directional growth movements of plants due to external
stimuli are called tropic movement. It can be either towards the
stimulus, or away from it. For example, in case of phototropic
movement, shoots respond by bending towards light while roots
respond by bending away from it.
41. What will happen if intake of iodine in our diet is low?
Ans.41. (a) When iodine intake is low, release of thyroxin from thyroid
gland will be less by which protein, carbohydrate and fat
metabolisms will be affected.
(b) A person might suffer from goitre in case of iodine deficiency
in the body.
42. What happens at the synapse between two neurons?
Ans.42. When an electrical signal reaches the axonal end of one neuron it
releases certain chemical substances that cross the synapse and
move towards the dendritic end of next neuron generating another
electrical signal.
43. Answer the following :
(a) Which hormone is responsible for the changes noticed in
females at puberty?
(b) Dwarfism results due to deficiency of which hormone?
(c) Blood sugar level rises due to deficiency of which hormone?
(d) Iodine is necessary for the synthesis of which hormone?
Ans.43. (a) Oestrogen
(b) Growth hormone
(c) Insulin
(d) Thyroxin
44. Answer the following :
(a) Name the endocrine gland associated with brain?
(b) Which gland secretes digestive enzymes as well as hormones?
(c) Name the endocrine gland associated with kidneys?
(d) Which endocrine gland is present in males but not in females?
Ans.44. (a) Pituitary
(b) Pancreas
(c) Adrenal
(d) Testes
45. Draw the structure of a neuron and explain its function.
Q46.What are the major parts of the brain? Mention the functions of
different parts.
Ans.Fore brain
Cerebrum- (i) Main thinking and largest part of the brain.
(ii) It has 3 main areas-
a. Sensory area- to receive impulses from sense organs viaReceptors
b. Motor area- control voluntary movements.
c. Association areas- Reasoning, learning & intelligence.
Different lobes of cerebrum –
Different lobes of cerebrum –
a) Frontal lobe – It is associated with reasoning .
b) Parietal – Perception of general sensation s like pressure, touch and pain.
c) Occipital – Visual perception.
d) Temporal – Important for interpreting sounds and the language we hear and formation of memories.
Thalamus – It relays sensory information to the Cerebrum
Hypothalamus- It forms the link between Nervous system & Endocrine system
Mid brain- It connects Fore brain and Hind brain. Controls reflex of eyes & ears
Hind brain- Connects the Fore brain & Hind brain
Cerebellum – Controls & coordinates muscular movements, maintaining body posture and equilibrium.
Pons- Acts as a bridge between brain & spinal cord
Medulla oblongata- Controls involuntary actions like blood pressure, salivation, vomiting, etc.
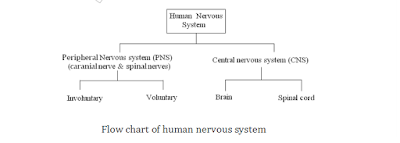
47. What constitutes the central and peripheral nervous systems? How
are the components of central nervous system protected?
Ans.
48. Mention one function for each of these hormones :
(a) Thyroxin
(b) Insulin
(c) Adrenaline
(d) Growth hormone
(e) Testosterone.
Ans.48. (a) Thyroxin regulates carbohydrate, fat and protein metabolisms
(b) Insulin — regulates blood sugar
(c) Adrenaline — increases heart rate and supply of blood to
various organs
(d) Growth hormone — regulates growth and development
(e) Testosterone — controls the changes of body features
associated with puberty in male
49. Name various plant hormones. Also give their physiological effects
on plant growth and development.
Ans.
50. What are reflex actions? Give two examples. Explain a reflex arc.
Ans. A reflex action is an involuntary response in the body to a stimulus. Many such actions in the body, from breathing to moving away from a hot object, are done without requiring thought. A group of neurons called a neuron arc cause the reflex action to occur; the neuron arc consists of the receptor, the sensory neuron, the interneuron, the motor neuron and the effector
Reflex Arc:It is the pathway followed by sensory nerve in carrying the sensation from receptor organ to spinal cord and then the pathway followed by motor nerve in carrying the order from spinal cord to effector organ during a reflex action.
51. “Nervous and hormonal systems together perform the function of
control and coordination in human beings.” Justify the statement.
Ans. A number of interactions between the environmen t and the animal are a result of combined action of both neurons and endocrine syste m for which specialized tissues are used to provide control and co – ordinations activities.
.52. How does chemical coordination take place in animals?
Ans.Different endocrine glands secrete different hormones. These
hormones are released into blood which carry them to specific
tissues or organs called target tissues or target organs. In the
target tissues, hormone triggers a particular biochemical or
physiological activity.
53. Why is the flow of signals in a synapse from axonal end of one
neuron to dendritic end of another neuron but not the reverse?
Ans.53. When an electrical signal reaches the axonal end of a neuron, it
releases a chemical substance. This chemical diffuses towards
the dendrite end of next neuron where it generates an electrical
impulse or signal. Hence, the electrical signal is converted into a
chemical signal at the axonal end. Since these chemicals are
absent at the dendrite end of the neuron the electrical signal,
cannot be converted into chemical signal.











No comments:
Post a Comment