Important Notes of LIGHT-REFLECTION & REFRACTION
Light is a form of energy, which enable us to see the object.
In this chapter we will study the phenomena of reflection and refraction using the
property of light i.e. straight line propagation (Light wave travel from one point to
another, along a straight line).
Reflection of Light
When the light is allowed to fall on highly polished surface, such as mirror, most of
the light gets reflected.
Laws of Reflection
1. The angle of incidence is always equal to angle of reflection.<i = <r
2. The incident ray, reflected ray and the normal to the reflecting surface at the
point of incidence lie in the same plane.
Properties of Image formed by Plane Mirror
1) Virtual (imaginary) & Erect (Virtual Þ The image that do not form on
screen.)
2) Laterally inverted (The left side of object appear on right side of image)
3) The size of image is equal to that of object
4. The image formed is as for behind the mirror as the object is in front of it.
Reflection of light by spherical MirrorsMirrors, whose reflecting surface are curved inward or outward spherically are
called spherical mirror.
For example - Spoon } ® The curved surface of shinning spoon can be considered
as curved mirror.
If it is curved inward ® Act as concave mirror
If it is curved outward ® Act as a convex mirror.
Few Basic terms related to Spherical Mirror
1. Principal axis : Line joining the pole and centre of curvature of the spherical mirror.
2. Pole : The geometrical central point of the reflecting spherical surface. (aperture), denoted by (P).
3. Aperture : The width of reflecting spherical surface.
4. Centre of curvature : The reflecting surface of a spherical mirror form a part of sphere. It has a centre, which is known as centre of curvature, denoted by (C)
5. Radius of curvature : The separation between the pole and the centre of curvature. ie. PC = R
6. Focus point : The point on the principal axis, where all parallel rays meet after reflection, denoted by (F) 7. Focal length : The length between the pole and focus point i.e. PF = f
8. Relationship between focal length and Radius of curvature.F=R/2
Image formation by spherical Mirror
Before we learn the formation of image or ray diagram, let us go through few tips
a) Remember, A ray of light which is parallel to principle axis always pass
through focus (meet at focus) or vice-versa
See the example of both concave and convex mirror when incident ray is parallel to principle axis or when it passes through focus
b) A ray of light which passes through centre of curvature (it is also known as
normal at the point of incidence on spherical mirror) will retrace their path
after reflection
Light is a form of energy, which enable us to see the object.
In this chapter we will study the phenomena of reflection and refraction using the
property of light i.e. straight line propagation (Light wave travel from one point to
another, along a straight line).
Reflection of Light
When the light is allowed to fall on highly polished surface, such as mirror, most of
the light gets reflected.
Laws of Reflection
1. The angle of incidence is always equal to angle of reflection.<i = <r
2. The incident ray, reflected ray and the normal to the reflecting surface at the
point of incidence lie in the same plane.
Properties of Image formed by Plane Mirror
1) Virtual (imaginary) & Erect (Virtual Þ The image that do not form on
screen.)
2) Laterally inverted (The left side of object appear on right side of image)
3) The size of image is equal to that of object
4. The image formed is as for behind the mirror as the object is in front of it.
Reflection of light by spherical MirrorsMirrors, whose reflecting surface are curved inward or outward spherically are
called spherical mirror.
For example - Spoon } ® The curved surface of shinning spoon can be considered
as curved mirror.
If it is curved inward ® Act as concave mirror
If it is curved outward ® Act as a convex mirror.
Few Basic terms related to Spherical Mirror
1. Principal axis : Line joining the pole and centre of curvature of the spherical mirror.
2. Pole : The geometrical central point of the reflecting spherical surface. (aperture), denoted by (P).
3. Aperture : The width of reflecting spherical surface.
4. Centre of curvature : The reflecting surface of a spherical mirror form a part of sphere. It has a centre, which is known as centre of curvature, denoted by (C)
5. Radius of curvature : The separation between the pole and the centre of curvature. ie. PC = R
6. Focus point : The point on the principal axis, where all parallel rays meet after reflection, denoted by (F) 7. Focal length : The length between the pole and focus point i.e. PF = f
8. Relationship between focal length and Radius of curvature.F=R/2
Image formation by spherical Mirror
Before we learn the formation of image or ray diagram, let us go through few tips
a) Remember, A ray of light which is parallel to principle axis always pass
through focus (meet at focus) or vice-versa
See the example of both concave and convex mirror when incident ray is parallel to principle axis or when it passes through focus
 c) A ray of light falling on pole get reflected at the same angle on the other side of
principal axis.
c) A ray of light falling on pole get reflected at the same angle on the other side of
principal axis.

Image formation by a concave mirror for different position of the object
The image will only form when two or more rays meets at apoint.
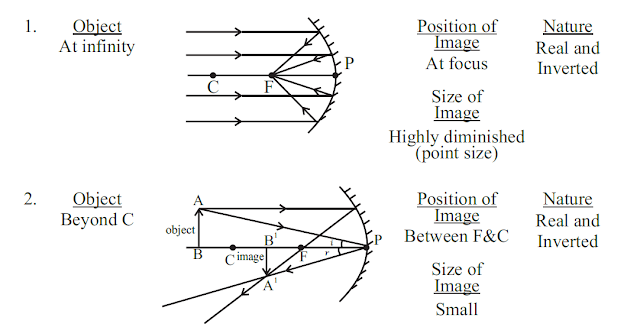




 Uses of Concave Mirror1. Used in torches, search light and headlight of vehicle.
Uses of Concave Mirror1. Used in torches, search light and headlight of vehicle.2. Used to see large image of face as shaving mirror
3. Used by dentist to see large images of the teeth
4. Large concave mirror used to focus sunlight (heat) in solar furnaces.
Uses of Convex Mirror1. Used as rear-view mirror in vehicles because it gives erect image. It also helps
the driver to view large area.
Sign Convention for Reflection by Spherical Mirror
1. The object is always placed to the left side of mirror.
2. All distance should be measured from pole (P); parallel to principal axis.
3. Take 'P' as origin. Distances measured
Right of the origin (+ x - Axis) are taken positive
Left of the origin (– x-Axis) are taken negative
Perpendicular to and above principal axis (+y-Axis) are taken positive
Perpendicular to and below principal axis (–y-Axis) are taken negative
A ray of light bends as it moves from one medium to another Refraction is due to change in the speed of light as it enters from one transparent medium to another.
Speed of light decreases as the beam of light travel from rarer medium to the denser medium.
Some Commonly observed phenomenon due to Refraction
1. The stone at the bottom of water tub appear to be raised.
2. A fish kept in aquarium appear to be bigger than its actual size.
3. A pencil partially immersed in water appears to be displaced at the interface of
air and water.
When a incident ray of light AO passes from a rarer medium (air) to a denser
medium (glass) at point. O on interface AB, it will bends towards the normal. At pt
O1, on interface DC the light ray entered from denser medium (glass) to rarer
medium (air) here the light ray will bend away from normal OO1is a refracted ray
OB is an emergent ray. If the incident ray is extended to C, we will observe that
emergent ray O1B is parallel to incident ray. The ray will slightly displaced laterally
after refraction.
Note : When a ray of light is incident normally to the interface of two media it will
go straight, without any deviation.
Laws of refraction of light-
1. The incident ray, the refracted ray and the normal to the interface of two
transparent media at the point of incidence, all lie in the same plane.
2. The ratio of sine of angle of incidence to the sine of angle of refraction is a
constant ie.


Spherical Lens A transparent material bound by two surface, of which one or both surfaces are spherical, forms a lens.
CONVEX LENS
A lens may have two spherical surfaces, bulging outwards, is called double convex lens (or simply convex lens. It is also known as converging lens because it converges the light.
CONCAVE LENS
A lens bounded by two spherical surfaces, curved inwards is known as double concave lens (or simply concave lens) It is also known as diverging lens because it diverges the light.
1. Centre of curvature - A lens, either a convex lens or a concave lens has two
spherical surfaces. Each of these surfaces form a part of sphere. The centre of
these two spheres are called centre of curvature represented by C and C . 1 2
2. Principal axis - Imaginary straight line passing through the two centres of
curvature
3. Optical Centre - The central point of lens is its optical centre (O). A ray of
light, when passes through 'O' it remains undeviated i.e. it goes straight.
4. Aperture - The effective diameter of the circular outline of a spherical lens.
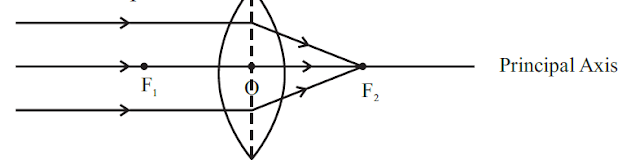
5. Focus of lens - Beam of light parallel is principal axis, after refraction from
1) Convex lens, converge to the point on principal axis, denoted by F,
known as Principal focus
2) Concave lens, appear to diverge from a point on the principal axis, known
as principal focus.
a) After refraction, a ray parallel to principal axis will pass through F.


Image formation by a convex lens for various position of object





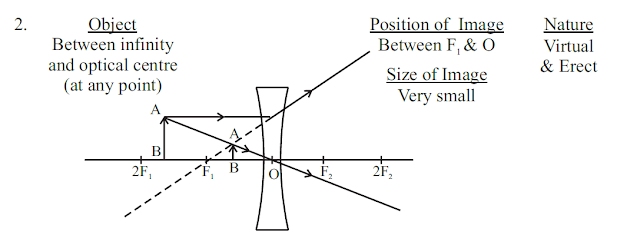
Sign Convention for Refraction by spherical lens
Similar to that of spherical mirror, only the difference is that all the measurement are made from optical centre 'O'














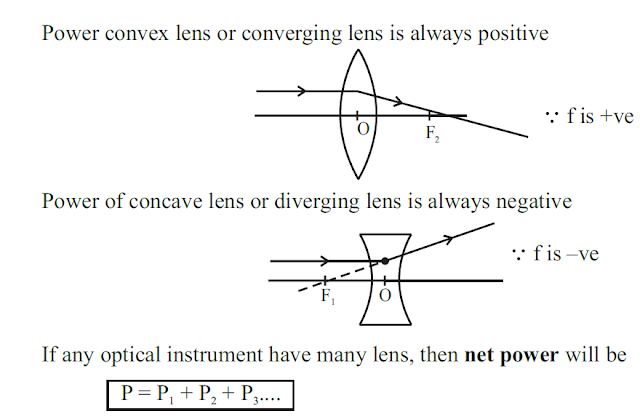



Reflection is called echo, refraction is called aberration
ReplyDeleteAn echo is the reflection of sound, it is hearing back of a sound by a listener after the sound has been heard for the first time, the delay in the echo is proportional to the distance between the listener and the reflecting surface, Reflection is called echo, refraction is called aberration
An echo is the reflection of sound, it is hearing back of a sound by a listener after the sound has been heard for the first time, the delay in the echo is proportional to the distance between the listener and the reflecting surface, http://sasuwaphysics.blogspot.com.ng/2017/03/how-are-reflection-and-refraction.html
This comment has been removed by the author.
ReplyDeleteIt is really a good note prepared for the students of India. But, the syllabus of Nepal is a little different than what is mentioned here. If you want to get fresh notes of Light chapter for Class 10 of Nepal, visit here:Light Class 10
ReplyDeletethanks for providing such a great article on light and reflection
ReplyDelete