Q1.How are acute diseases different from chronic diseases?
Ans:Acute disease – Diseases which last for short periods of time and are severe are called acute diseases.
Chronic disease – Diseases which are long lasting are called chronic diseases.
Q2.What is the full form of AIDS? Name the causal organism.
Ans.AIDS – Acquired Immuno deficiency syndrome It is caused by HIV – Human Immuno deficiency virus.
Q3.State two conditions essential for keeping good health
Ans:Conditions for keeping good health are
(a) Public and personal hygiene
(b) Regular exercise, sleep and relaxation.
(c) Proper habits.
(d) Nutrition
Q4.Define (a) health (b) disease.
Ans.Health – It is defined as a state of complete physical, mental and social well being
and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity.
Disease – A disease in the malfunctioning of body organs due to one reason or
the other.
Q5.Why are antibiotics not effective for viral disease
Ans.Antibiotics block the bacterial pathways wthout affecting the pathways of humans. In the case of viruses, they have very few
biochemical pathways of their own. They use the metabolic machinery of host and grow and reproduce.
Q6.What is inflammation? What are the changes occur during inflammation?
Ans.It is the recruitment process by immune system in which immune system recruits many cells to the affected tissue to kill the disease causing germs. During this process, certain local effects such as swelling and pain and general effects such as fever may develop.
Q7.Why do some children fall ill more frequently than others living in the same locality?
Ans.Diseases can be prevented by –
(a) By presenting exposure to disease causing microbes – For this, exposure to over crowded areas can be avoided, source of drinking water must be checked, and we must provide clean environments.
(b) By consuming proper and sufficient food / balanced diet.
(c)By immunization.
Q8. What are noncommunicable diseases? Give examples.
Ans.Those diseases which can not be spread from person to person for e.g Diabetes, Cancer etc
Q9.Define Carriers.give two examples
Ans.Carriers are the organisms which harbor disease-causing germs without showing
away sign of disease themselves, but have the ability to infect other healthy individuals.
For Example – Housefly, female insect Anopheles.
Q10.Why do Children require Vaccination
Ans.Children are more vulnerable and susecptible to diseases and are hence given vaccines so they are able to develop immunity against diseases.
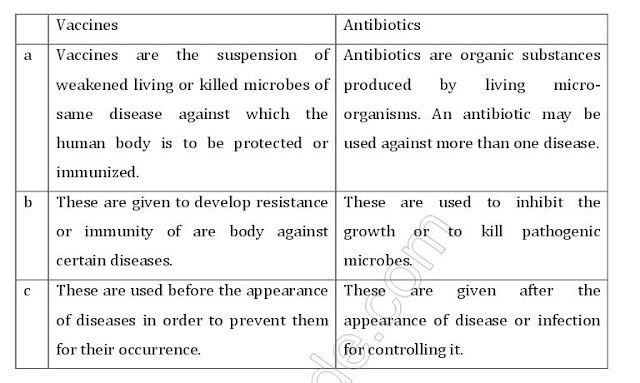
Q11.Give difference between vaccines and antibiotics.
Ans.
Q12.The body of a patient has lost its power of fighting against infections. Which disease may the patient be suffering from? Name the pathogen and describe any two modes of its transmission from the patient to other person.
Ans.Patient is suffering from AIDS.
It is caused by HIV (Human Immuno deficiency Virus) Modes of transmission are
(1) By sexual contact with infected person.
(2) By the use infected syringe.
Q13.What are the means of spread of Diseases
Ans.Diseases spread through –
(1) Air – When an infected person sneezes or coughs or spits, a healthy person standing nearby can inhale these droplets, causing infection in that person.
(2) By water – Some diseases can spread from one person to another when a sick person’s stools gets into water. The people drinking the infected water thus get the disease.
(3) By physical contact – Some of the diseases like AIDS, syphilis and gonorrhea spread by sexual contact. These diseases are not transmitted by casual physical contact like handshakes, hug’s, sports like wrestling and other ways in which we touch other socially.
Q14.What are the various dimensions of health?
Ans.Various dimensions of health are –
a) Physical dimensions Physical health implies ‘perfect functioning of all the organs and systems of the body.
b) Mental dimension – Mental health implies a state of balance and harmony between the individual and surrounding world.
c) Social dimension – A person is socially healthy if he has a good job, a good house, a happy family, good neighbors and understanding friends.
Q15.What are the causes of diseases?
Ans.Causes of diseases are –
a) Infection by micro – organisms – Bacteria, virus, fungi, protozoa and worms cause communicable diseases.
b) Malfunctioning of body organs.
c) Deficiency of one or more nutrients.
d) Genetic factors
e) Polluted environment.
Q16.Which bacterium causes peptic ulcers? Who discovered the above pathogen?
Ans.Peptic ulcer is caused by bacterium Helicobacter pylori, it was discovered by Robin warren and Barry Marshall.
Q17.What are the conditions favoring for air-bone diseases?
Ans.Conditions favoring for air-borne infections -
a) Close proximity to the infected person.
b) Over – crowding
c) Poor – Ventilation
Q18. What are the different types of diseases?Explain them.
Ans.Diseases are broadly grouped into two types
–
a) Communicable or infectious disease – Those diseases which are passed on from one person to another in various ways through air, water, food, physical contact and insects.
b) Non-communicable diseases – Those diseases which cannot be spread from person to Peron. Forex - arthritis, marasmus etc.
Q19.Name the target organs for the following disease-
(a) Hepatitis targets ______________
(b) Fits or unconsciousness targets __________________
(C) Pneumonia targets _________________
(d) Fungal disease targets ______________
Ans. a) liver
b) Brain
c) lungs
d) skin
Q20.What is immunization, immune system, immunity?
Ans. Immunization is a specific method of preventing diseases by inoculating vaccines in the human body.
Immune system – It is a system which protect are body against infection
Immunity – The body’s power to resist and overcome infection is called immunity.
Q21.Who discovered ‘vaccine’ for the first time? Name two diseases which can be prevented by using vaccine.
Ans.Vaccines were first developed by Edward Jenner for the treatment of smallpox. Polio and Tuberculosis can be prevented by using vaccine.
Q22.Name the approaches generally adopted to treat infectious diseases.
Ans.There are two approaches to treat the infections diseases. These are –
a) To reduce the effects of the disease.
b) To eliminate or kill the cause of the disease.
Q23.Explain giving reasons –
(a) Balanced diet is necessary for maintaining health body.
(b) Health of an organism depends upon the surrounding environmental conditions.
Ans.a) Balanced diet contain all the nutrient required for maintaining proper health as well as needed for growth and repair. Lack of single nutrient causes deficiency diseases.
B)Surrounding environmental conditions plays an important role in the
maintenance of health. For ex we feel depressed if
–(i) surrounding are dirty or polluted
(ii) garbage is not collected or disposed off
(iii) drains are not cleaned and water collects in the streets or open spaces. Unclean surrounding causes the entry of germs via air, water, food or vectors and makes the person unhealthy.
Q24.What are the different aspects of maintaining good health?
Ans.Different aspects for maintaining good health-
a) Community health – It involves all the factorsrelating to personal health
along with the services necessary for providing good health for the community.
b) Personal health (hygiene) It is the science of preserving and promoting health mainly through the active efforts of an individual. It is practiced through active, sanitary habits and healthy way of life.
c) Exercise, relaxation and sleep. Regular exercise is very necessary to keep the body fit. Proper sleep of about 6-8 hours is essential, Relaxation is very essential for good health.
d) Nutrition – Optimum nutrition is essential formaintenance of good health. One should take sufficient and balanced food for maintaining good health.
Q25.Name the agents and the diseases caused by them?
Ans.
Q26.What are the different aspects of maintaining good health?
Ans.Different aspects for maintaining good health-
a) Community health – It involves all the factors relating to personal health
along with the services necessary for providing good health for the community.
b) Personal health (hygiene) It is the science ofpreserving and promoting
health mainly through the active efforts of an individual. It is practiced
through active, sanitary habits and healthy way of life.
c) Exercise, relaxation and sleep. Regular exercise is very necessary to keep the body fit. Proper sleep of about 6-8 hours is essential, Relaxation is very
essential for good health.
d) Nutrition – Optimum nutrition is essential for maintenance of good health. One should take sufficient and balanced food for maintaining good health.
Ans:Acute disease – Diseases which last for short periods of time and are severe are called acute diseases.
Chronic disease – Diseases which are long lasting are called chronic diseases.
Q2.What is the full form of AIDS? Name the causal organism.
Ans.AIDS – Acquired Immuno deficiency syndrome It is caused by HIV – Human Immuno deficiency virus.
Q3.State two conditions essential for keeping good health
Ans:Conditions for keeping good health are
(a) Public and personal hygiene
(b) Regular exercise, sleep and relaxation.
(c) Proper habits.
(d) Nutrition
Q4.Define (a) health (b) disease.
Ans.Health – It is defined as a state of complete physical, mental and social well being
and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity.
Disease – A disease in the malfunctioning of body organs due to one reason or
the other.
Q5.Why are antibiotics not effective for viral disease
Ans.Antibiotics block the bacterial pathways wthout affecting the pathways of humans. In the case of viruses, they have very few
biochemical pathways of their own. They use the metabolic machinery of host and grow and reproduce.
Q6.What is inflammation? What are the changes occur during inflammation?
Ans.It is the recruitment process by immune system in which immune system recruits many cells to the affected tissue to kill the disease causing germs. During this process, certain local effects such as swelling and pain and general effects such as fever may develop.
Q7.Why do some children fall ill more frequently than others living in the same locality?
Ans.Diseases can be prevented by –
(a) By presenting exposure to disease causing microbes – For this, exposure to over crowded areas can be avoided, source of drinking water must be checked, and we must provide clean environments.
(b) By consuming proper and sufficient food / balanced diet.
(c)By immunization.
Q8. What are noncommunicable diseases? Give examples.
Ans.Those diseases which can not be spread from person to person for e.g Diabetes, Cancer etc
Q9.Define Carriers.give two examples
Ans.Carriers are the organisms which harbor disease-causing germs without showing
away sign of disease themselves, but have the ability to infect other healthy individuals.
For Example – Housefly, female insect Anopheles.
Q10.Why do Children require Vaccination
Ans.Children are more vulnerable and susecptible to diseases and are hence given vaccines so they are able to develop immunity against diseases.
Q11.Give difference between vaccines and antibiotics.
Ans.
Q12.The body of a patient has lost its power of fighting against infections. Which disease may the patient be suffering from? Name the pathogen and describe any two modes of its transmission from the patient to other person.
Ans.Patient is suffering from AIDS.
It is caused by HIV (Human Immuno deficiency Virus) Modes of transmission are
(1) By sexual contact with infected person.
(2) By the use infected syringe.
Q13.What are the means of spread of Diseases
Ans.Diseases spread through –
(1) Air – When an infected person sneezes or coughs or spits, a healthy person standing nearby can inhale these droplets, causing infection in that person.
(2) By water – Some diseases can spread from one person to another when a sick person’s stools gets into water. The people drinking the infected water thus get the disease.
(3) By physical contact – Some of the diseases like AIDS, syphilis and gonorrhea spread by sexual contact. These diseases are not transmitted by casual physical contact like handshakes, hug’s, sports like wrestling and other ways in which we touch other socially.
Q14.What are the various dimensions of health?
Ans.Various dimensions of health are –
a) Physical dimensions Physical health implies ‘perfect functioning of all the organs and systems of the body.
b) Mental dimension – Mental health implies a state of balance and harmony between the individual and surrounding world.
c) Social dimension – A person is socially healthy if he has a good job, a good house, a happy family, good neighbors and understanding friends.
Q15.What are the causes of diseases?
Ans.Causes of diseases are –
a) Infection by micro – organisms – Bacteria, virus, fungi, protozoa and worms cause communicable diseases.
b) Malfunctioning of body organs.
c) Deficiency of one or more nutrients.
d) Genetic factors
e) Polluted environment.
Q16.Which bacterium causes peptic ulcers? Who discovered the above pathogen?
Ans.Peptic ulcer is caused by bacterium Helicobacter pylori, it was discovered by Robin warren and Barry Marshall.
Q17.What are the conditions favoring for air-bone diseases?
Ans.Conditions favoring for air-borne infections -
a) Close proximity to the infected person.
b) Over – crowding
c) Poor – Ventilation
Q18. What are the different types of diseases?Explain them.
Ans.Diseases are broadly grouped into two types
–
a) Communicable or infectious disease – Those diseases which are passed on from one person to another in various ways through air, water, food, physical contact and insects.
b) Non-communicable diseases – Those diseases which cannot be spread from person to Peron. Forex - arthritis, marasmus etc.
Q19.Name the target organs for the following disease-
(a) Hepatitis targets ______________
(b) Fits or unconsciousness targets __________________
(C) Pneumonia targets _________________
(d) Fungal disease targets ______________
Ans. a) liver
b) Brain
c) lungs
d) skin
Q20.What is immunization, immune system, immunity?
Ans. Immunization is a specific method of preventing diseases by inoculating vaccines in the human body.
Immune system – It is a system which protect are body against infection
Immunity – The body’s power to resist and overcome infection is called immunity.
Q21.Who discovered ‘vaccine’ for the first time? Name two diseases which can be prevented by using vaccine.
Ans.Vaccines were first developed by Edward Jenner for the treatment of smallpox. Polio and Tuberculosis can be prevented by using vaccine.
Q22.Name the approaches generally adopted to treat infectious diseases.
Ans.There are two approaches to treat the infections diseases. These are –
a) To reduce the effects of the disease.
b) To eliminate or kill the cause of the disease.
Q23.Explain giving reasons –
(a) Balanced diet is necessary for maintaining health body.
(b) Health of an organism depends upon the surrounding environmental conditions.
Ans.a) Balanced diet contain all the nutrient required for maintaining proper health as well as needed for growth and repair. Lack of single nutrient causes deficiency diseases.
B)Surrounding environmental conditions plays an important role in the
maintenance of health. For ex we feel depressed if
–(i) surrounding are dirty or polluted
(ii) garbage is not collected or disposed off
(iii) drains are not cleaned and water collects in the streets or open spaces. Unclean surrounding causes the entry of germs via air, water, food or vectors and makes the person unhealthy.
Q24.What are the different aspects of maintaining good health?
Ans.Different aspects for maintaining good health-
a) Community health – It involves all the factorsrelating to personal health
along with the services necessary for providing good health for the community.
b) Personal health (hygiene) It is the science of preserving and promoting health mainly through the active efforts of an individual. It is practiced through active, sanitary habits and healthy way of life.
c) Exercise, relaxation and sleep. Regular exercise is very necessary to keep the body fit. Proper sleep of about 6-8 hours is essential, Relaxation is very essential for good health.
d) Nutrition – Optimum nutrition is essential formaintenance of good health. One should take sufficient and balanced food for maintaining good health.
Q25.Name the agents and the diseases caused by them?
Ans.
Q26.What are the different aspects of maintaining good health?
Ans.Different aspects for maintaining good health-
a) Community health – It involves all the factors relating to personal health
along with the services necessary for providing good health for the community.
b) Personal health (hygiene) It is the science ofpreserving and promoting
health mainly through the active efforts of an individual. It is practiced
through active, sanitary habits and healthy way of life.
c) Exercise, relaxation and sleep. Regular exercise is very necessary to keep the body fit. Proper sleep of about 6-8 hours is essential, Relaxation is very
essential for good health.
d) Nutrition – Optimum nutrition is essential for maintenance of good health. One should take sufficient and balanced food for maintaining good health.




No comments:
Post a Comment